Technological advances and the development of complex instrumentation have necessitated purified environments to avoid contaminating components and parts from atmospheric particles and bacteria. Clean rooms were developed in the middle of the 20th Century to create the ideal tool for providing conditions for the production, manufacture, and fabrication of modern technological tools and instruments. Read More…
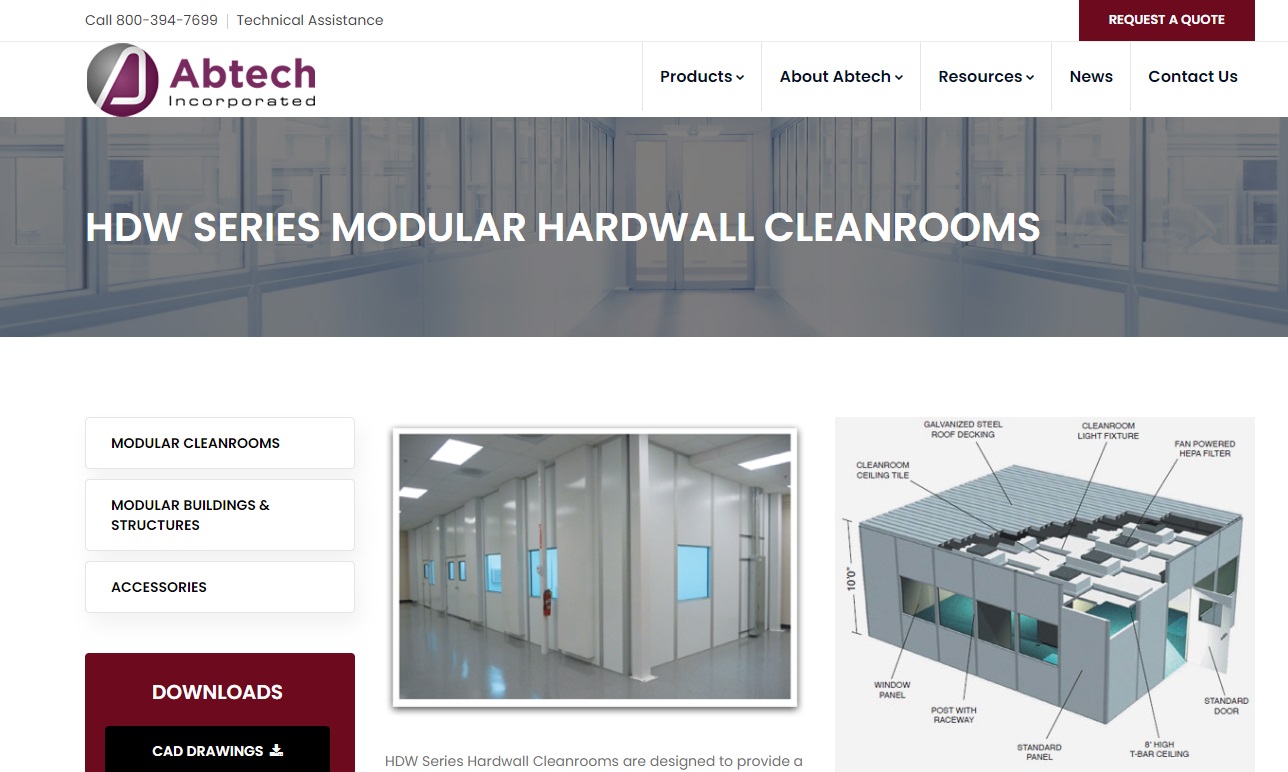
As a manufacturer of clean rooms, including inplant modular offices, exterior steel buildings, guard buildings, fork liftable and crane liftable buildings, multi-level buildings and mezzanines, Abtech offers turnkey installations or packages for install by end user. Our modular structures are constructed of steel, are free-standing & manufactured under strict quality control methods.
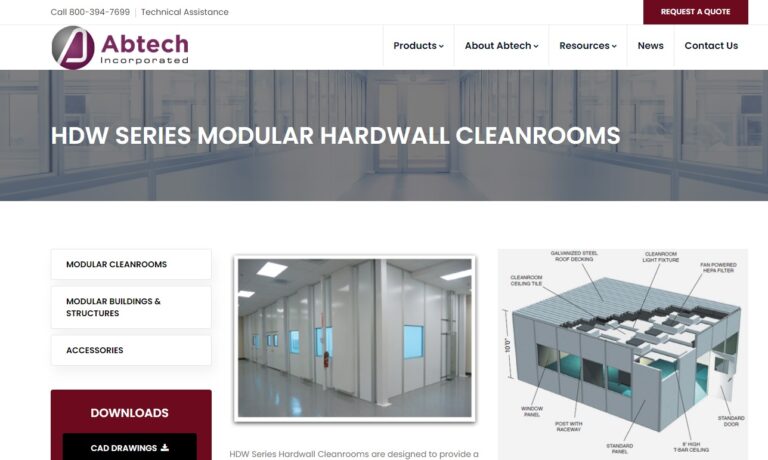
For the very best of clean rooms, look no further than Clean Rooms International! We can provide the ultimate in quality, customer service, durability, and unique designs just for you!
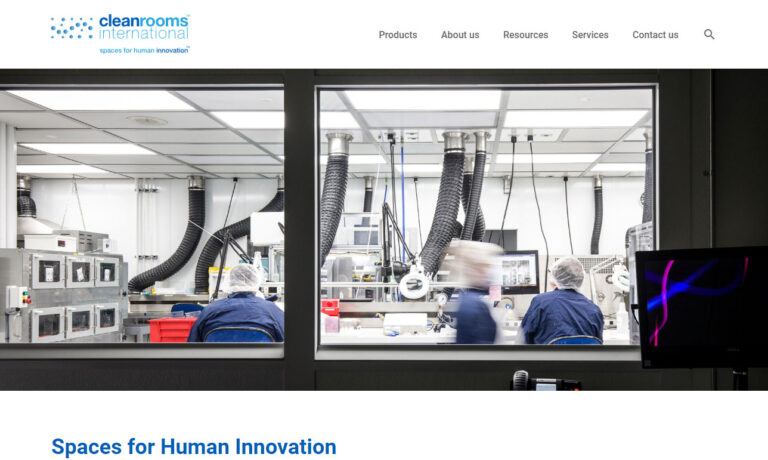
Cleanrooms By United is the industry’s premier manufacturer of modular clean room systems. We design, manufacture and install our clean rooms to meet our customers’ unique requirements. The custom, flexible, modular construction of our cleanrooms makes them easy to expand, reconfigure, or relocate as your cleanroom needs evolve.
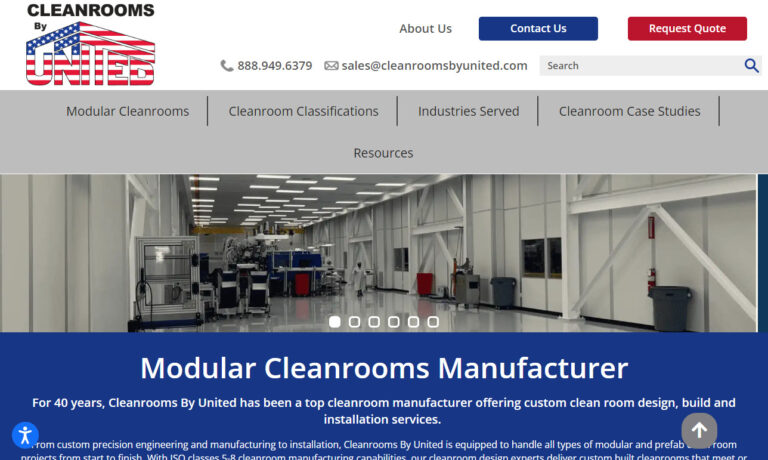
Atmos-Tech Industries is a designer and manufacturer of cleanrooms and equipment for industries, including health care, pharmaceutical aerospace and automotive.
At MayAir Inc., we specialize in designing, engineering, and manufacturing high-performance clean rooms tailored to meet the most stringent contamination control requirements. With years of expertise, we provide comprehensive clean room solutions for various industries, including pharmaceuticals, electronics, biotechnology, and healthcare.

Our complete line of clean rooms will meet your needs. We are the experts of the clean room industry and our engineers can work with you to determine which clean room models work best for your business. We offer a variety of softwall, bio-clean, hardwall, and micro-clean options, all of which are manufactured with the highest standards. You will not be upset with our products. Contact us for more ...
Since 1976, we at Mitchell Technical Sales have been dedicated to delivering excellence in quality cleanroom design, manufacturing, installation, certification, and maintenance. Our journey has been marked by innovation and expertise, ensuring that every project we undertake reflects our commitment to precision and cutting-edge solutions.

More Cleanroom Design Manufacturers
What Is a Clean Room? Cleanroom Standards, Classifications, and Design
The term clean room (or cleanroom) refers to a specially engineered and meticulously controlled environment that has been cleansed of dust, dirt, microbes, and other contaminating particles. Cleanrooms are used extensively across industries like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, semiconductor manufacturing, aerospace, medical device production, food processing, and scientific research—any application where contaminant control is critical to operational success. To be classified as a clean room, specific standards and conditions must be met, as stipulated by the United States Government's Federal Standard 209 (FED-STD-209E) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO 14644-1). These cleanroom standards define the maximum allowable levels of airborne particulate contamination and provide a universal system for cleanroom classification.
Understanding the cleanroom classification system and the essential requirements for contamination control is the first step in evaluating, designing, or selecting a cleanroom for your organization or project. Whether you are searching for a modular cleanroom solution, a permanent facility, or a portable cleanroom, it is crucial to match the facility to your process requirements and regulatory obligations.
Clean Room Standards: ISO vs. FED-STD-209E
The description of the standards of the ISO and Federal Standard 209 clearly and concisely defines the conditions a clean room must meet to be classified as a clean room. Adhering to the qualifications is the initial step in the process, followed by determining what classification a clean room meets.
Although the ISO and Federal Standard 209 intend to define the class of a clean room, each organization approaches the issue using a different classification method. For the ISO, clean rooms are classified using a numbering system, beginning with ISO 1 for the strictest compliance with clean room standards and continuing to ISO 9. Federal Standard 209 was published by the Institute of Environmental Sciences and Technology (IEST) in 1963 and was updated in 1992. Its numbering system begins with class 1 (ISO 3) as the most restricted and continues to class 100,000.
The process of designing a cleanroom begins with determining what classification is necessary. The primary factor in deciding is based on the size and quantity of particulate matter allowed in the air, which is essential for defining a clean room's classification. These classifications are critical for industries where even microscopic particles can affect product quality, yield, or safety.
ISO 14644-1 Cleanroom Standards Table
| Maximum Particles/m³ | |||||||
| Classification | ≥0.1µm | ≥0.2µm | ≥0.3µm | ≥0.5µm | ≥1µm | ≥5µm | FED STD 209E Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 1 | 10 | 2.37 | 1.02 | 0.35 | 0.083 | 0.0029 | |
| ISO 2 | 100 | 23.7 | 10.2 | 3.5 | 0.83 | 0.029 | |
| ISO 3 | 1,000 | 237 | 102 | 35 | 8.3 | 0.029 | Class 1 |
| ISO 4 | 10,000 | 2,370 | 1,020 | 352 | 83 | 2.9 | Class 10 |
| ISO 5 | 100,000 | 23,700 | 10,200 | 3,520 | 832 | 29 | Class 100 |
| ISO 6 | 1.0 x 10^6 | 237,000 | 102,000 | 35,200 | 8,320 | 293 | Class 1,000 |
| ISO 7 | 1.0 x 10^7 | 2.37 x 10^6 | 1,020,000 | 352,000 | 83,200 | 2,930 | Class 10,000 |
| ISO 8 | 1.0 x 10^8 | 2.37 x 10^7 | 1.02 x 10^7 | 3,520,000 | 832,000 | 29,300 | Class 100,000 |
| ISO 9 | 1.0 x 10^9 | 2.37 x 10^8 | 1.02 x 10^8 | 35,200,000 | 8,320,000 | 293,000 | Room Air |
Federal Standard 209 Air Classification System
The particles measured in a clean room are far smaller and more minute than the types of pollen, dust, and dirt that can be seen with the naked eye. Clean room particles are measured in micrometers, or one-thousandth of a millimeter, and referred to as a micron (µ). Understanding the micron scale is essential for anyone involved in contamination control, pharmaceutical production, electronics assembly, or medical device manufacturing.

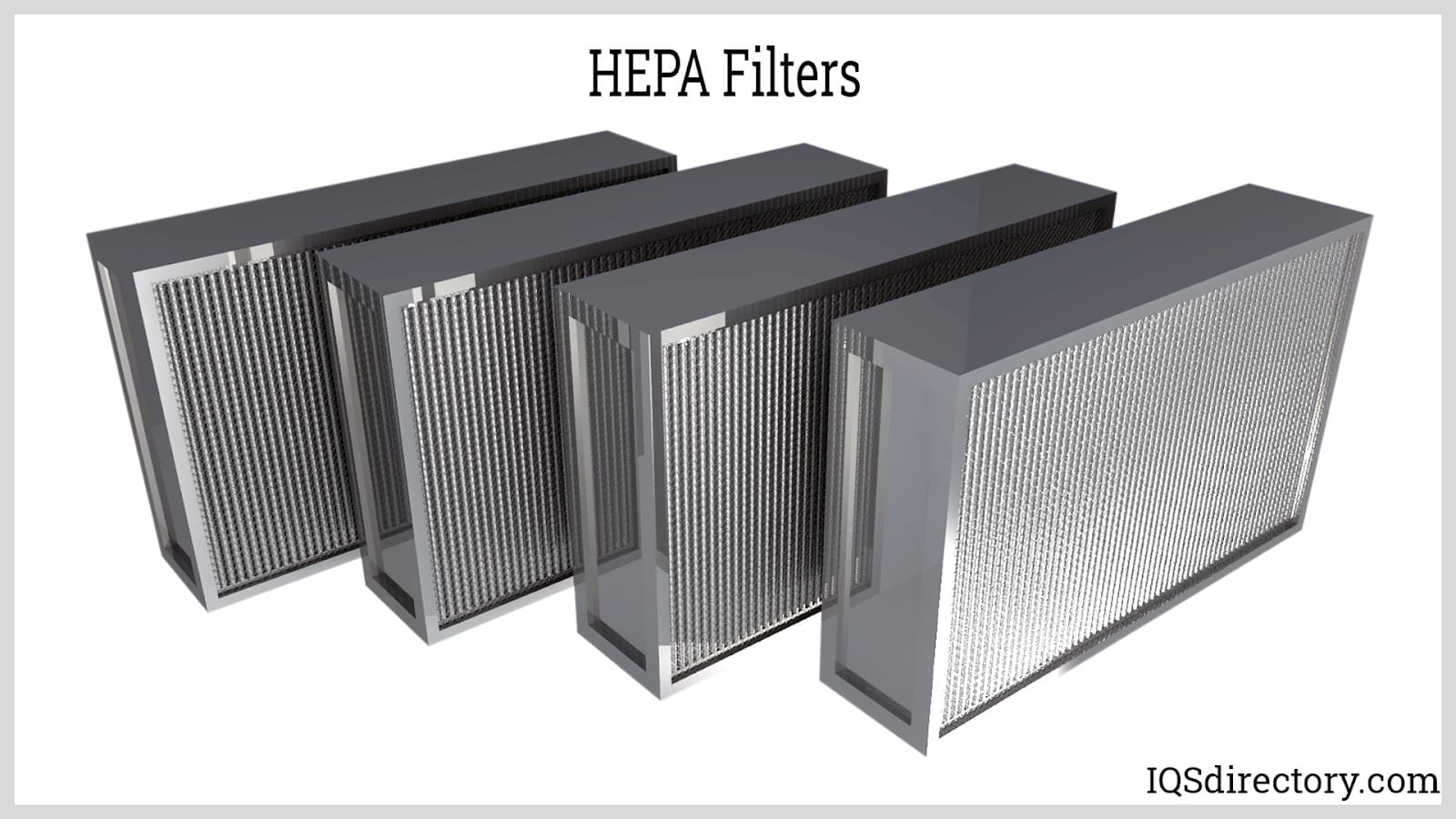
The US FED STD 209E standard system rates clean rooms based on the number of 0.5-micron particulates present per cubic foot in an enclosure. The particulate volume number decides the classification number assigned to a clean room. For example, Class 1 clean rooms have no more than one 0.5 micron particle per cubic foot. To achieve this low level of contamination, Class 1 clean room designs must have high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters working in concert with other decontamination equipment.
As the class numbers increase, so does the acceptable level of particulate presence. For example, Class 10,000 clean rooms contain no more than 10,000 0.5 micron sized particles per cubic foot. By comparison, the normal unfiltered air we breathe would be Class 1,000,000. This highlights the dramatic reduction in contaminants that cleanrooms provide over ordinary environments.
The lower the class number, the more likely the clean room has hard walls with a complex filtration and personnel decontamination system. Higher-class clean rooms, such as modular and portable cleanrooms, can be less permanent. They provide basic protection and can be moved easily and disassembled without difficulty. Choosing the right cleanroom class depends on your application's sensitivity and the required level of contamination control.
The design and structure of a clean room dictate the kinds of operations for which it can be used. This is also represented through the garments workers are permitted to wear. For example, Class 1 clean rooms require employees to wear a bunny suit covering them from head to toe with a mask and synthetic gloves. In Class 10,000 clean rooms, workers can wear their own clothes but must have their hair, feet, hands, and faces covered. Additionally, Class 1 clean rooms are small and limited to allow for better air supply control, while Class 10,000 clean rooms can be very large, like classrooms.
Frequently Asked Questions About Clean Room Standards and Classes
- What is the difference between ISO and FED-STD-209E cleanroom standards?
ISO standards use metric units and are recognized internationally, providing a universal system for cleanroom classification. FED-STD-209E is an older American standard based on imperial units and has been largely superseded by ISO 14644-1. - How do I determine which cleanroom class I need?
The required cleanroom class depends on your application's sensitivity to contamination, regulatory requirements, and industry best practices. Conduct a risk assessment and consult with experienced cleanroom design engineers. - Can cleanrooms be upgraded or modified?
Yes. Modular cleanroom systems and customizable components allow for cleanroom upgrades, retrofits, and reclassification to meet evolving contamination control needs. - What industries require cleanrooms?
Cleanrooms are used in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, medical device manufacturing, electronics/semiconductors, aerospace, food processing, healthcare, and scientific research, among others.
Elements of a Clean Room
Three basic principles are considered when planning and designing a clean room. The first of those considerations is the quality of the air, which is the determining factor regarding a clean room's classification. Next is the size and number of surfaces of a clean room and the type of equipment used. The final component, and the one that supplies the most contamination, is the number of workers. Below, we explore these elements in detail to help you make informed decisions when specifying or designing a cleanroom.
Air Filtration and Circulation Systems
The key element when defining a clean room is its quality of air. Controlling fresh air flow is simple since it involves passing a stream of air through a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration system. In ultra-clean environments, ultra-low penetration air (ULPA) filters may also be required. The challenge is how to maintain that system without the clean room being contaminated. This aspect of the design process is the key to a high-performance clean room.
Each classification of clean rooms measures the air change rate (ACR), determined by how quickly the air in a clean room is replaced by clean filtered air. The ACR is the number of air changes per hour, with lower-class clean rooms having an ACR measured in changes per second. Additionally, the speed of the change is measured in feet per minute. For instance, semiconductor cleanrooms may require hundreds of air changes per hour, while a pharmaceutical compounding cleanroom may have a lower rate, depending on the class and process risk.

Knowing what atmosphere the industry requires is necessary when planning a clean room. Particle size and the number of particles in a cubic foot or meter must be carefully assessed regarding the product being tested or fabricated. For example, medical device assembly may require ISO 7, while nanotechnology or microelectronics manufacturing may require ISO 5 or lower.
Key Questions to Ask When Specifying Cleanroom Air Quality
- What is the minimum particle size that needs to be controlled for your process?
- What are the acceptable levels of viable and non-viable particulates?
- Is positive or negative pressure required to contain or exclude particulates?
- Do you require humidity, temperature, or electrostatic control as well?
Clean Room Structure and Materials
Once the air filtration and cleanliness have been established, the next step is to design the walls, ceiling, floor, vents, and entryways for a clean room. Wall panels are made of resilient materials that are tightly secured. Ceilings have a metal hanging grid where tiles are securely placed. Finally, vents can be located on the floor or walls for easy airflow. Modern cleanrooms often use modular construction for flexibility and ease of expansion.
Cleanroom construction materials are chosen for their ability to resist particle shedding, ease of cleaning, and chemical resistance. Common materials include powder-coated steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and special cleanroom-rated plastics or composites. Flooring is often seamless vinyl, epoxy, or other anti-static materials to prevent dust accumulation and facilitate cleaning protocols.

Entryways, such as airlocks and pass-through chambers, are vital for maintaining pressure differentials and minimizing outside contamination. Cleanrooms may be equipped with sticky mats, HEPA-filtered air showers, and gowning rooms to further reduce particulate ingress.
Cleanroom Options: Modular, Hardwall, and Softwall
- Modular Cleanrooms: Flexible, expandable, and quick to deploy; ideal for changing production needs.
- Hardwall Cleanrooms: Permanent structures providing robust contamination control and higher pressure differentials; suited for high-criticality environments.
- Softwall Cleanrooms: Cost-effective, quickly installed, and easily relocated; best for less stringent applications or temporary needs.
Personnel and Contamination Control Protocols
The final element in clean room planning is the people who will work in it. Air control, clean walls and ceilings, and the seal of a clean room are static and seldom change. However, the personnel is constantly changing and carries a wide range of contaminants and bacteria, which must be monitored and controlled through body coverings, masks, and decontamination doors and pass thrus. The classification of a clean room determines the type of hygiene clean room staff must follow. Cleanroom gowning procedures and protocols are crucial for maintaining compliance and protecting product integrity.
Best practices for personnel include:
- Wearing appropriate cleanroom garments (coveralls, hoods, booties, gloves, masks)
- Following strict hand hygiene and gowning procedures
- Minimizing movement and talking inside the cleanroom
- Limiting the number of personnel and time spent in critical areas
- Training staff regularly on contamination control measures and protocols
Applications and Industries Using Cleanrooms
Cleanrooms are essential for any process where the presence of airborne particles, microbes, or chemical vapors could compromise product quality, research outcomes, or patient safety. They support a wide range of applications, including:
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Aseptic production of drugs, compounding sterile preparations, vaccine manufacturing, and quality control testing.
- Biotechnology: Cell and tissue culture, genetic engineering, and development of biologics.
- Medical Device Assembly: Implantable devices, surgical instruments, catheter assembly, and packaging in sterile environments.
- Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing: Wafer fabrication, microchip assembly, and precision optics production where even microscopic particles can ruin yields.
- Aerospace and Defense: Satellite assembly, propulsion systems, optics, and avionics requiring ultra-clean assembly spaces.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Specialized cleanrooms for high-risk food production to prevent cross-contamination and ensure product safety.
- Research Laboratories: Molecular biology, nanotechnology, and analytical chemistry labs requiring controlled environments.
- Healthcare: Hospital operating rooms, compounding pharmacies, and isolation units.
Looking for a cleanroom tailored to your industry? Explore cleanroom solutions by industry and application to learn more about specialized designs and regulatory considerations.
Benefits of Cleanrooms and Controlled Environments
Implementing a cleanroom environment provides tangible advantages for organizations requiring strict contamination control. Key benefits include:
- Consistent Product Quality: Reduces defects, improves yield, and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meets standards enforced by FDA, EMA, ISO, and other regulatory bodies for critical manufacturing and research.
- Protection of Personnel and Processes: Safeguards workers, sensitive products, and processes from harmful contaminants.
- Operational Efficiency: Reduces production downtime due to contamination events, enables faster time-to-market.
- Enhanced Reputation: Demonstrates commitment to quality, safety, and innovation to customers and regulators.
How to Choose the Right Clean Room for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate cleanroom solution involves a careful evaluation of your application requirements, regulatory obligations, and operational workflow. Consider the following decision factors:
- Cleanroom Classification: What ISO or FED-STD-209E class is necessary for your process?
- Size and Layout: What are your space constraints, workflow, and future expansion plans?
- Type of Construction: Is a modular, hardwall, or portable cleanroom best for your needs?
- Air Handling Requirements: How many air changes per hour, and what level of filtration is needed?
- Utility Integration: Do you require cleanroom-compatible HVAC, electrical, process gases, or data connectivity?
- Compliance and Validation: What documentation, validation, and environmental monitoring are required for regulatory or customer audits?
- Budget and Timeline: What is your available budget and required timeline for installation and commissioning?
Still have questions? Contact a cleanroom design expert or request a quote to get personalized guidance for your project.
Selecting the Right Clean Room Design Company
For the most productive outcome when purchasing a clean room design from a clean room design company, it is important to compare several businesses using our directory of clean room design companies. Each clean room design company has a business profile page that highlights their areas of expertise and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with them for more information or to request a quote. Review each clean room design business using our patented website previewer to get a better understanding of what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple clean room design businesses with the same form.
How to Find the Best Clean Room Supplier or Manufacturer
- Search for companies with extensive experience in your industry and required cleanroom class.
- Ask for case studies, validation documentation, and references for completed projects.
- Request detailed proposals and compare pricing, lead times, and after-sales support.
- Consider companies offering turnkey solutions, including design, engineering, installation, commissioning, and training.
- Evaluate their ability to provide ongoing maintenance, certification, and environmental monitoring services.
Explore More Cleanroom Resources
Looking to deepen your understanding? Discover more about cleanroom validation, maintenance, and environmental monitoring on our website, or reach out to our experts for tailored consultation and project support.













 Calibration Services
Calibration Services Clean Rooms
Clean Rooms Data Acquisition Systems
Data Acquisition Systems Dynamometers
Dynamometers Environmental Test Chamber
Environmental Test Chamber Leak Detectors
Leak Detectors Load Cells
Load Cells Machine Vision Systems
Machine Vision Systems Scales
Scales Thermocouples
Thermocouples Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services